HANDYREHAB
Affordable Robotics for Rehabilitation
Innovation
Integrity
Excellence
Efficacy
Featured Products



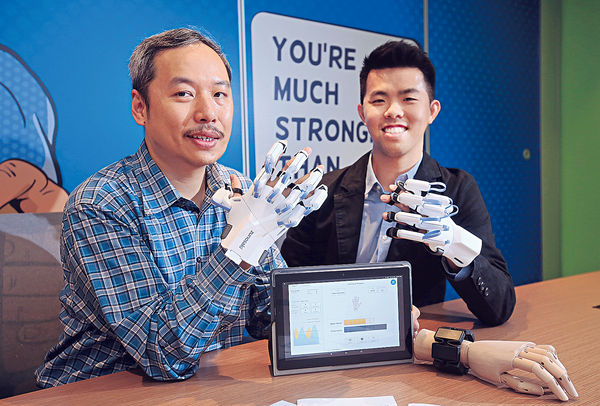
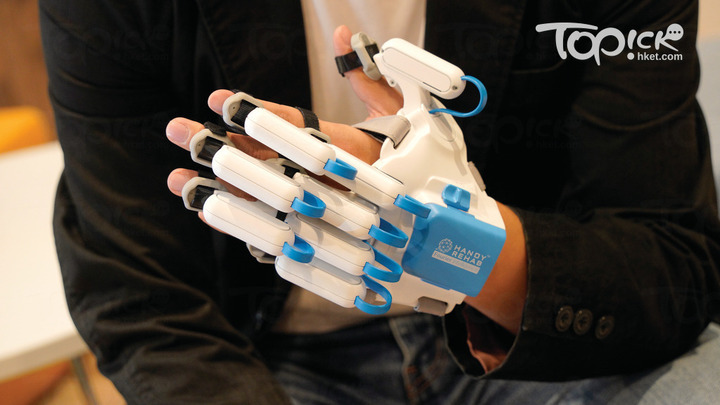
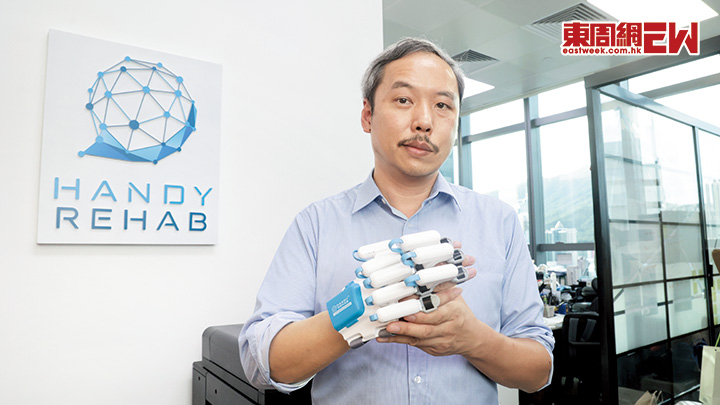
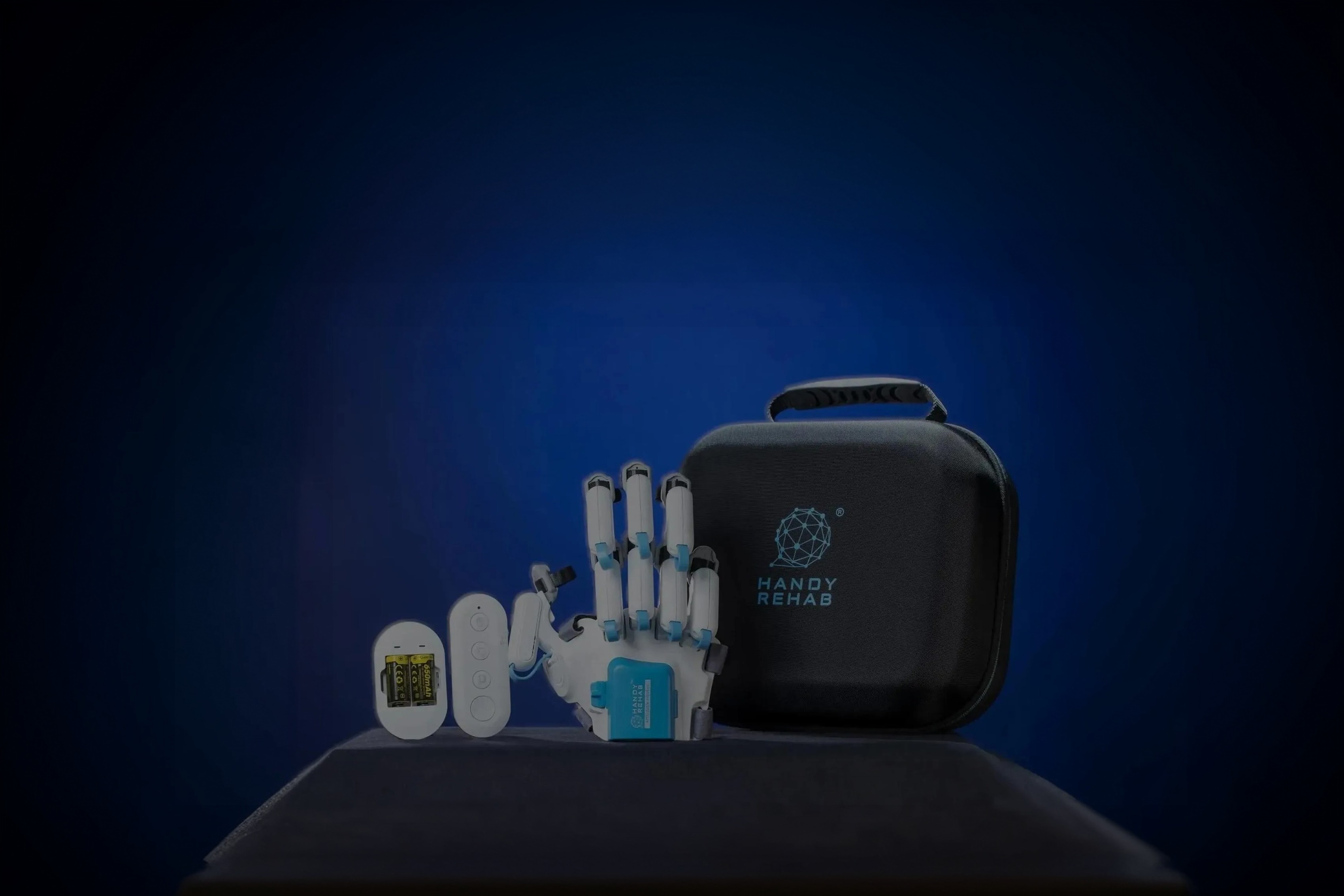
HandyRehab - Home Edition
Home-based training device for stroke rehabilitation
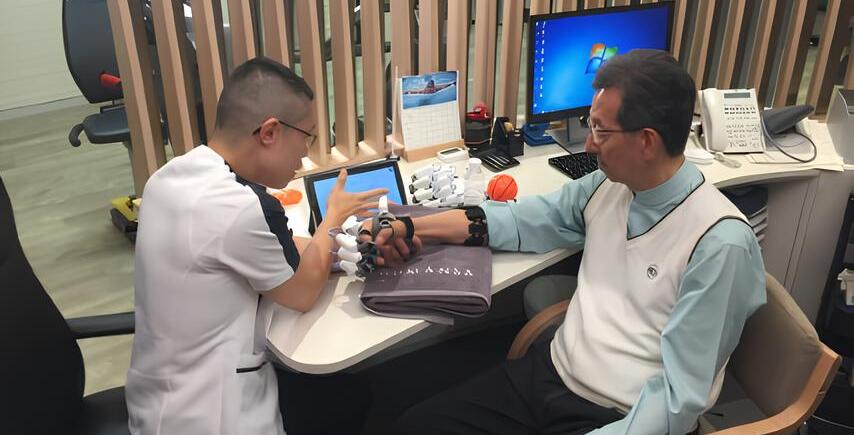
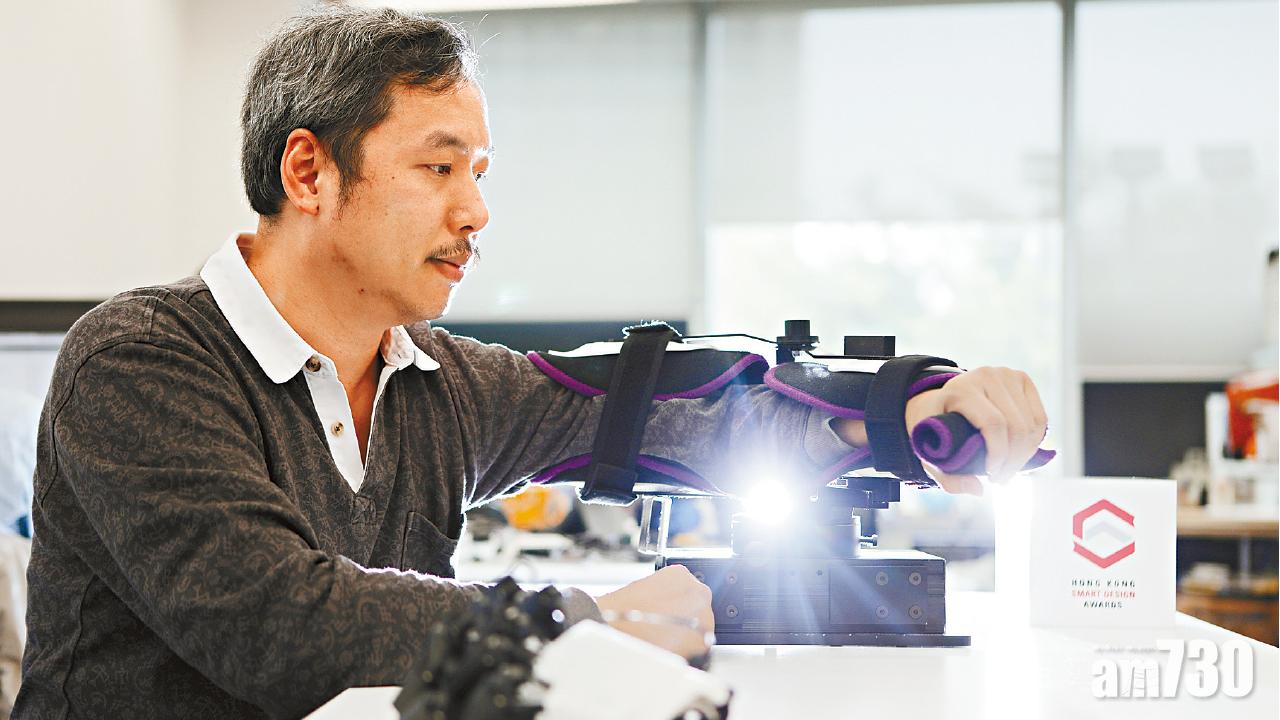
HandyRehab Home Edition is specifically designed to meet the upper limb rehabilitation needs of stroke patients. Utilizing the latest technology in mechanical engineering, it provides patients with different levels of training.
Product Features
Passive Training
Power up with our passive training device for ultimate convenience.
Portable
Take your essentials on the go with our sleek and portable device.
Wireless Design
Experience quality without any connections and fast response.
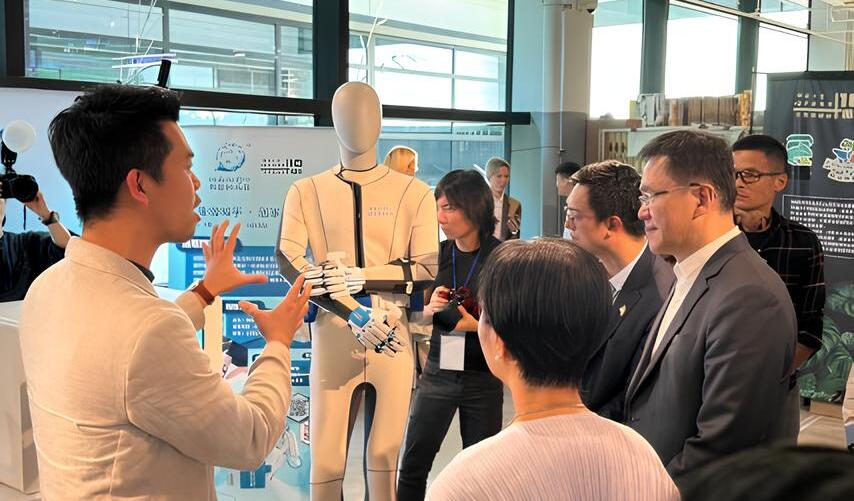
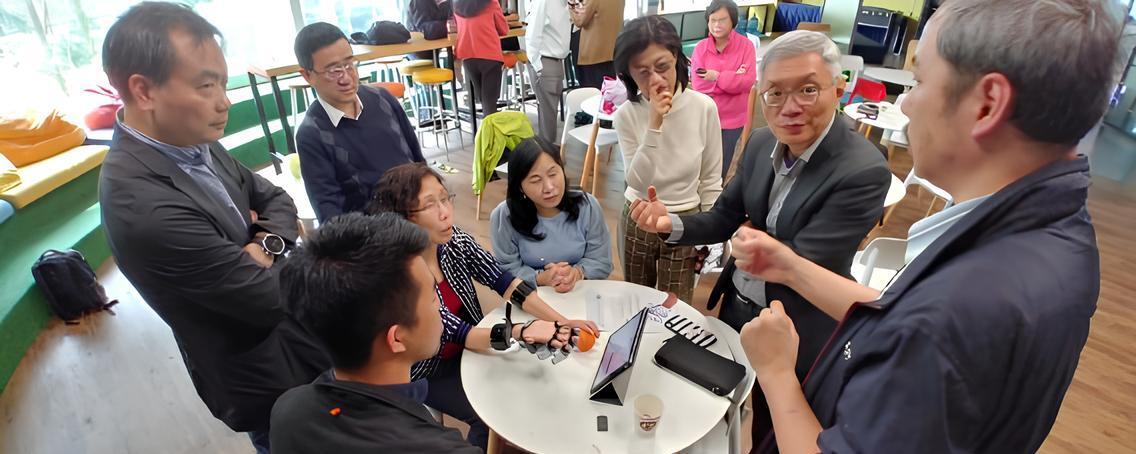
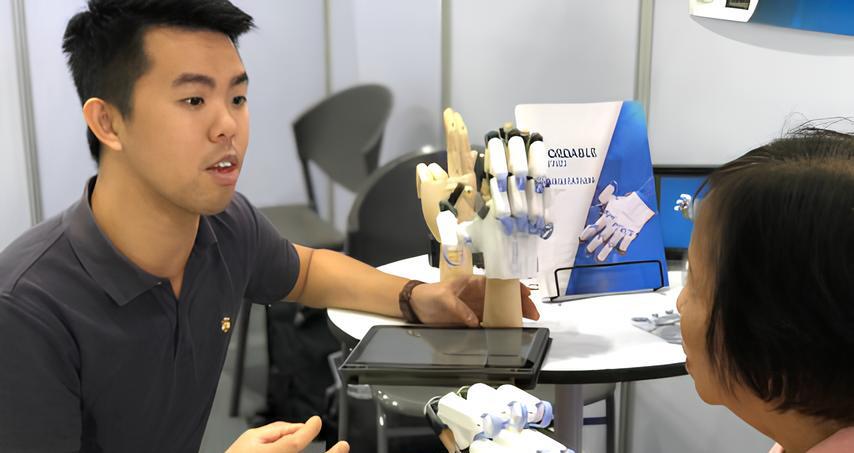
Media Exposure
User comments
Mr Choi, Senior Physiotherapist at Private Clinic
With the aid of HandyRehab System, therapists can visualise patients’ muscle activities during different actions. Allowing us to have a more objective assessment of patients’ rehabilitation progress.
Mr Chan, Physiotherapist at NGO
Traditional therapeutic methods emphasize repetitive exercises. Therapists instruct patients to complete an action until they can finally execute it correctly. However, neither the therapy nor the patients are certain whether the correct set of muscles is being used. With the robotic exoskeleton system, patients can now receive accurate feedback on their performance, which can greatly reduce the duration of training. Stroke patients, especially younger ones, are very eager to regain their hand function because they would love to be able to return to work.
Rolando, Physiotherapist
A patient told me that after using the robotic glove, he felt the connection between his brain and his hand. At the onset of his stroke, he felt as if his hand did not belong to him and could not be controlled. The characteristic feature of the robotic hand is that it trains the patient to use their brain to initiate hand movements. Even when a patient's muscle strength is very weak, the robotic hand can assist them. Patients can start with passive training, progress to semi-active training, and finally advance to active training. During this process, the patient can see that his hand can be controlled by himself.